Discover what is behind some blushed cheeks that seem to refuse to go away, may be the first step in understanding a deeper problem: couperoseThis skin condition may be damaging the health of your skin without you noticing, making it more and more sensitive and vulnerable.
In it García-Legaz Dermatological Institute, we understand how frustrating it can be to deal with this condition. That's why we want to address what couperose is, its causes, how it manifests itself and, most importantly, how you can treat it to restore the balance and well-being of your skin.
What is couperose?
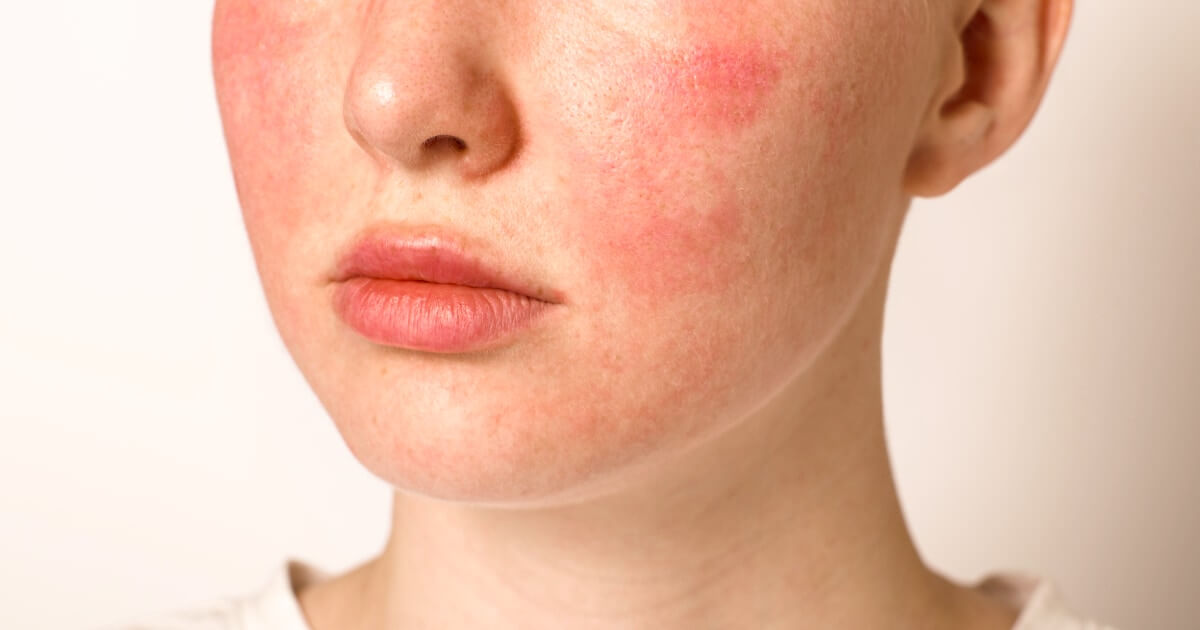
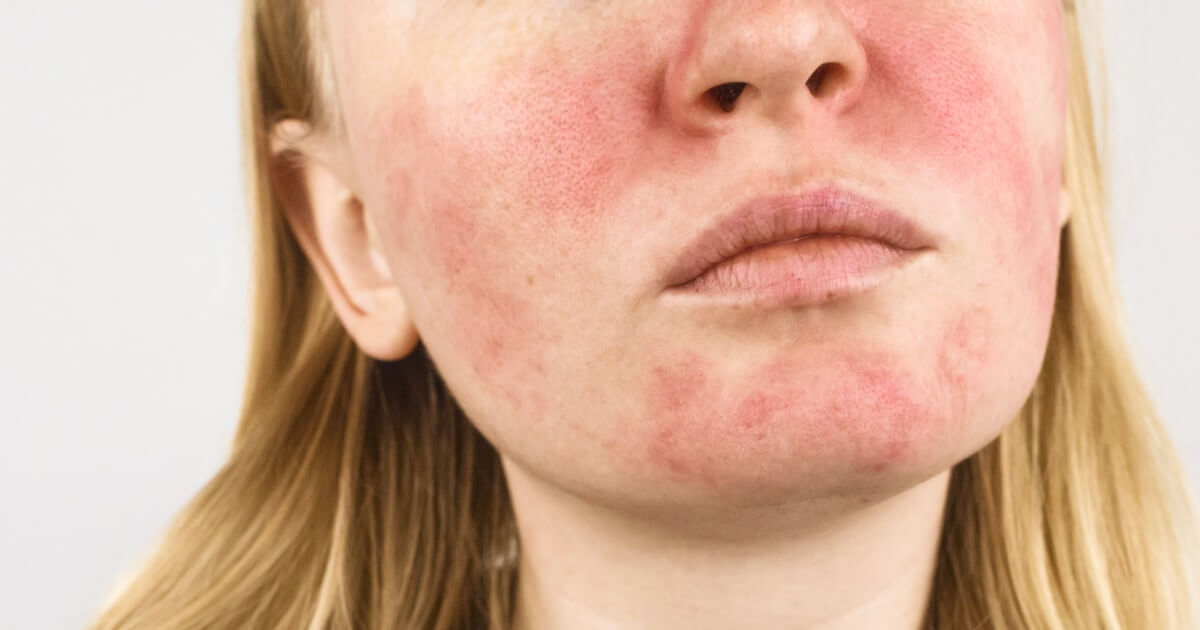
Couperose is a dermatological condition characterized by the dilation of small blood vessels, which causes a diffuse and persistent redness on the skin, especially in the face. It is more common in people with light and sensitive skin, which is more reactive to external stimuli.
“Although it does not pose a serious health risk, couperose can cause aesthetic concern and be a sign of skin sensitivity either underlying vascular problems.”
A diagnosis and treatment Appropriate medications are essential to control your symptoms, since, if left untreated, couperose can worsen and become chronic. In addition, it is important to evaluate your possible relationship with other conditions, as rosacea.
Main features
The demonstrations Symptoms of couperose vary among individuals, but generally include:
- Capillary dilation: dilated blood vessels cause visible redness on the skin.
- Persistence: Without treatment, the redness may become permanent.
- Additional symptoms: It is possible to experience sensations of numbness, tightness, itch either burning in the affected area.
- Variability: the episodes of redness may fluctuate and intensify due to factors such as weather, stress, certain foods or drinks, and temperature changes.
- Telangiectasias: the presence of small visible veins (telangiectasias), known as “spider veins”, which accentuate the redness.
Most affected areas
Cuperosis mainly affects the face, being more evident in exposed areas to changes in temperature and other environmental factors, such as:
- Cheeks.
- Nose.
- Chin.
Causes of couperose
Couperose, in addition to being influenced by genetic factors, can be triggered by various reasons. Identifying the underlying causes is critical to your prevention and management.
Below, we explain the factors most common factors that contribute to its appearance:
Climatic factors
The sudden changes in temperature have a significant impact on the skin, especially in people prone to couperose.
Exposure to extreme temperatures, whether cold or hot, can cause dilation of blood vesselsCold causes vasoconstriction, but sudden contact with heat causes capillaries to dilate abruptly, worsening facial redness.
In addition, the strong wind can irritate the skin and dehydrate its protective barrier, making it more vulnerable.
Hormonal changes
The hormonal fluctuations can affect the blood circulation and increase fragility of the glasses.
These alterations, common during menstruation, pregnancy or menopause, generate an increase in blood volume, which makes the dilation of the vessels more visible and contributes to facial redness.
Alcohol and tobacco consumption
These habits are important factors in the development of couperose.
He alcohol causes vasodilation, which increases blood flow to the skin and causes redness. tobacco, on the other hand, affects the oxygenation of the skin, compromising the health of blood vessels and promoting the appearance of spider veins.
Sun exposure
Solar radiation can be another significant trigger.
A inadequate exposure to UV rays weakens capillaries, making them more likely to break and cause redness.
Stress and intense emotions
He stress It has been linked to numerous alterations in skin health, and couperose is no exception.
In addition, the strong emotions, such as anger or embarrassment, can cause blood vessels to dilate, exacerbating facial redness in people with couperose.
Food and hot drinks
The consumption of extremely hot or spicy foods or drinks can increase the body temperature and dilate the blood vessels in the face, causing an immediate increase in blood flow and contributing to redness.
Topical irritants
Using harsh cosmetics, cleansers that strip the skin of its natural oils, and overly harsh exfoliants can weaken the protective barrier of the skin, causing irritation and worsening facial redness.
Prevention of couperose
To prevent couperose in susceptible people, it is essential take action that reduce the appearance of symptoms and keep the skin in good condition:
- Use sun protection Broad spectrum with SPF 50 daily.
- Avoid aggressive products with alcohol or strong fragrances, opting for gentle and moisturizing cleansers with soothing ingredients like vitamin B3.
- Avoid the prolonged exposure and the sudden changes in temperature and uses humidifiers in winter.
- Follow one diet balanced rich in antioxidants and adopt healthy habits
- Practice techniques of stress management and do exercise regularly.
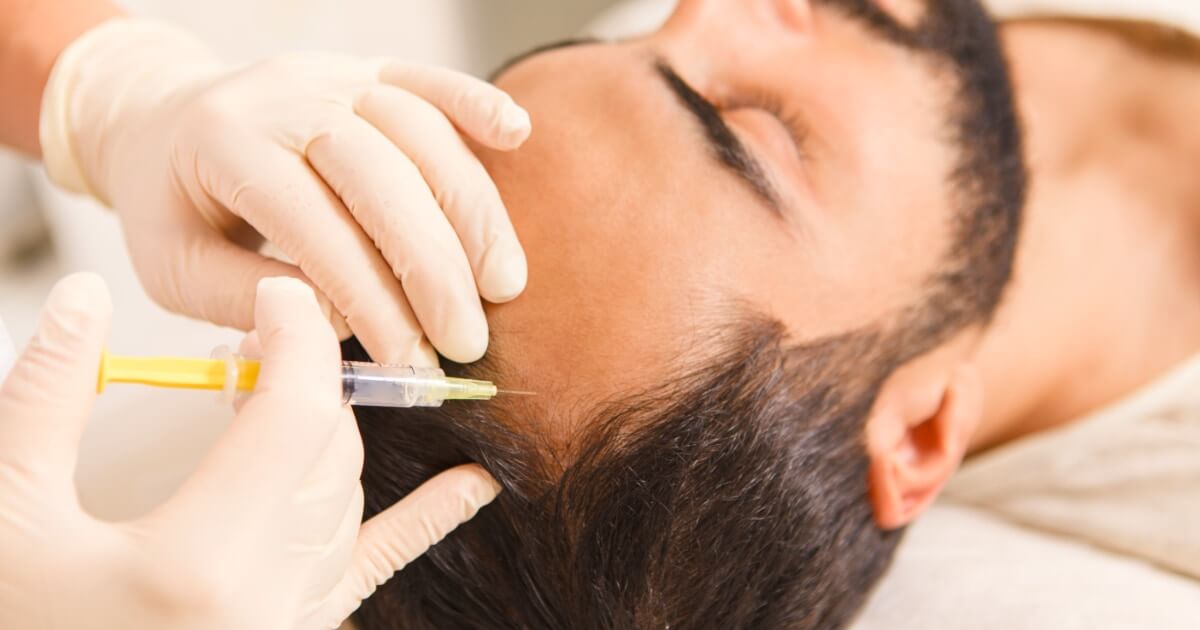
Laser treatment of couperose
In addition to using gentle cosmetic products and avoiding triggering factors, the laser treatment of couperose it is an option effective to reduce redness and control your symptoms.
“The laser uses light pulses controlled that are absorbed by the hemoglobin, the natural component present in the blood responsible for transporting oxygen.”
By absorbing light, hemoglobin transforms it into heat, which causes a controlled damage on the walls of the dilated blood vessels, causing coagulation and subsequent natural reabsorption.
At the García Legaz Dermatological Institute we trust in the advanced Nordlys platform, technology recognized for its precision and ability to minimize possible side effects, ensuring safe and effective treatment.
In short, couperose is a condition that can significantly affect the appearance and well-being of your skin, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, symptoms can be controlled and improved. Our specialists in dermatology They care about offering you a personalized approach and advanced technology to restore the balance and health of your skin.
Literature
- Codina, A. (2006). Cuperosis: etiology, prevention and treatment. Offarm: pharmacy and society, 25(10), 80-84. https://dialnet.unirioja.es
- Conte, L., Di Marco, K., Serra, N., De Monserrat, R., Distante, F., & Bonfigli, A. (2010). Long-term evaluation of the efficacy of a treatment for grade I erythrosis, couperose and/or rosacea. Fur, 25(7), 376-382. https://www.sciencedirect.com
- Condori-Diburga, H. (2002). Laser in dermatology. Peruvian Journal of Dermatology, 12(2). https://sisbib.unmsm.edu.pe