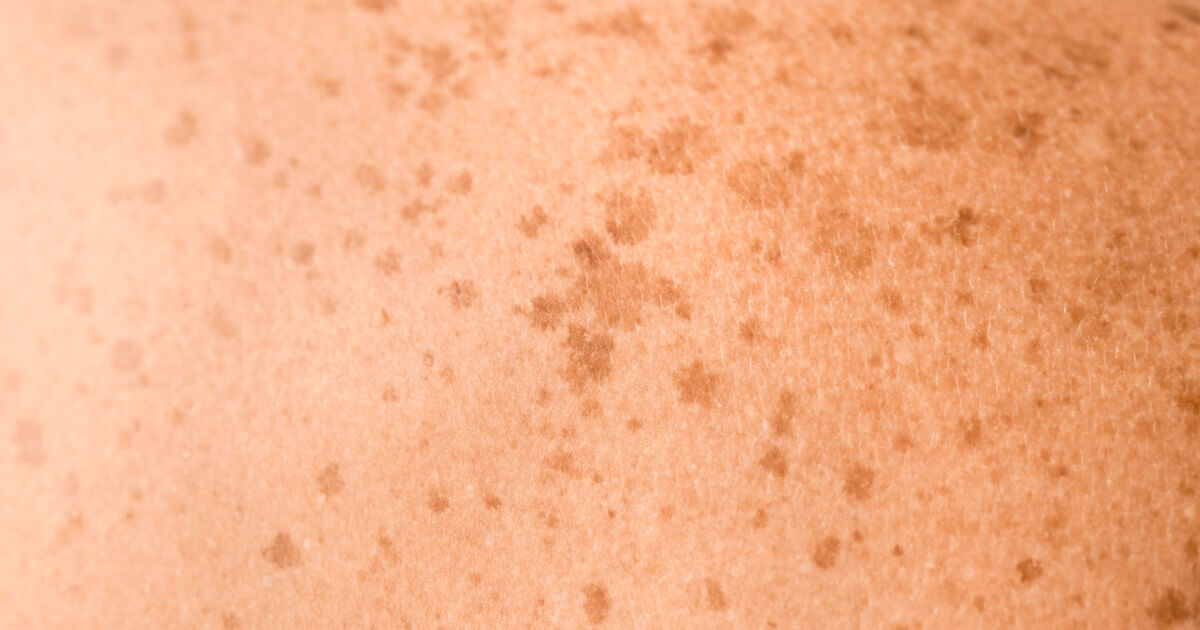
He lentigo solar is a common skin condition that manifests as dark spot on the skin, resulting from cumulative sun damage over time. Their presence not only indicates significant deterioration of the epidermis, but can also negatively affect the appearance of our skin and be aesthetically annoying.
In this post, from the García-Legaz Dermatological Institute We want to tell you how you can treat them and, most importantly, how to prevent their appearance so that you maintain a even and healthy skin over the years.
Origin and characteristics of the solar lentigo
The solar lentigo, commonly known as “sunspot”, is a pigmented lesion which is developed mainly by the prolonged and cumulative exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which stimulates the production of melamine on the skin.
This type of hyperpigmentation usually appears from the age of 40 in areas frequently exposed to the sun, such as:
- Face.
- Hands.
- Neckline.
- Arms.
Solar lentigines vary in size, from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter, and its coloration ranges from light to dark brown.
Over time, the skin's ability to regenerate decreases, which favors the appearance and persistence from solar lentigines. Therefore, it is essential to take appropriate protective measures to prevent or reduce the risk of developing these skin lesions.
Differences with other skin spots
Solar lentigo is often described as a flat, well-defined spot, which distinguishes it from others pigmentation disordersBelow, we list some of the characteristics that distinguish them:
- Freckles or ephelides: Freckles are more common in the childhood and they usually to clarify with reduced sun exposure.
- Malignant lentigo/melanoma: the stains malignant, like the melanoma, may present irregularities in shape, size and color, even a sensation of itching or bleeding.
- Senile lentigo: Although they are often confused, senile lentigo is more closely related to natural aging of the skin and cannot be attributed solely to sun exposure. It appears in people of advanced age and has characteristics similar to those of solar lentigines.
- Melasma: light brown spots that are frequently located on the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip, especially in women, due to hormonal causes (pregnancy, contraceptives, etc.), genetics, and in relation to sun exposure
- Seborrheic keratosis: benign warty lesions, usually brown in color, that can appear anywhere on the body but also on the face. It is most common in adults and has a significant genetic component.
The accurate identification of these characteristics is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
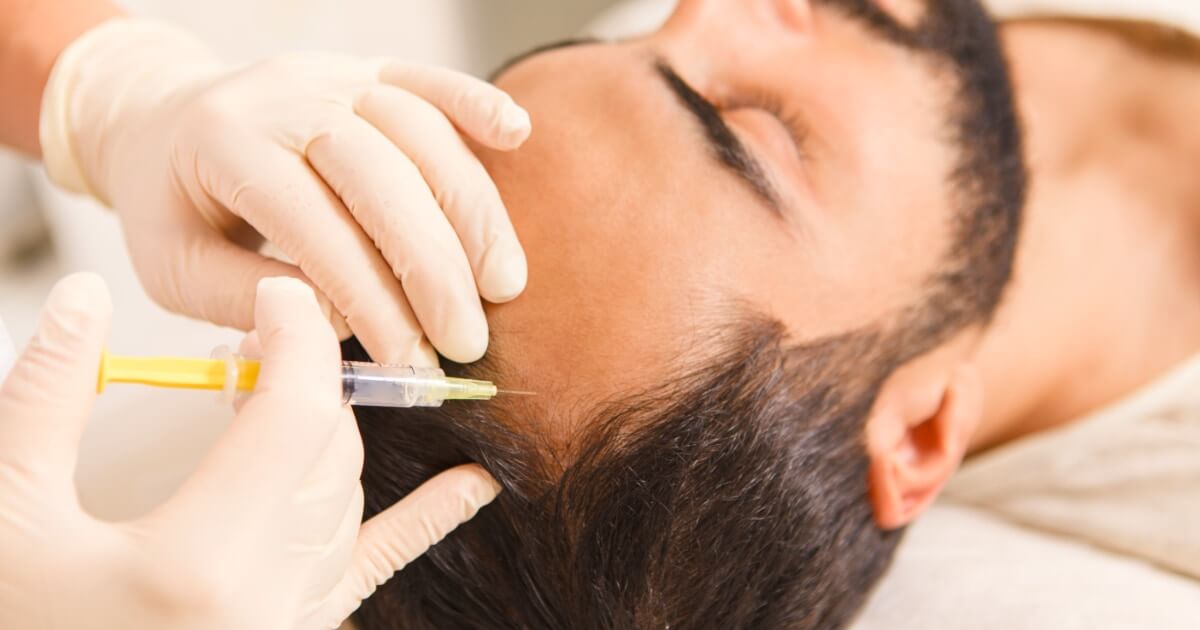
Treatment of solar lentigo
He treatment Solar lentigo treatment seeks to reduce or eliminate the appearance of these spots on the skin. To achieve this, there are various options, which include topical treatments and advanced dermatological procedures, such as laser. Below, we discuss these two methods.
Topical treatments
The topical treatments are usually one of the first options that are considered to address solar lentigo. It consists of applying creams directly to the affected areas and their effectiveness can vary depending on the case, it is therefore important that your dermatologist prescribes a personalized routine for you.
Among the most creams common are:
- Depigmenting agents: formulations, whose main active ingredient is usually the hydroquinone, which are designed to inhibit melanin production and clarify the stains.
- Antioxidants: ingredients such as vitamin C either glycolic acid can improve the appearance of spots thanks to their anti-inflammatory and lightening propertiesIts regular application helps to unify the skin tone and strengthen it.
Light sources and dermatological lasers
One of the treatments more effective To eliminate solar lentigines is the intense pulsed light.
At the García-Legaz Dermatological Institute we have the Nordlys platform, which uses technology Ellipse SWT, characterized by its bands of narrower wavelengths and precise compared to other IPLs.
These procedures destroy pigmented cells on the skin and promote its regeneration, which helps unify your skin's basic tone. Depending on your skin's photoaging, type of lesions, and your phototype, we will choose the most suitable wavelength for you or we will combine several of them.
It is usually performed on the entire face, several sessions spaced over weeks, improving lentigines from the first session. It's a virtually painless treatment with a quick recovery.
It is essential to avoid tanning before the session, and to use SPF 50 sunscreen both before and after the intense pulsed light treatment.
Prevention of solar lentigo
The prevention is clue to reduce the appearance of solar lentigines or malignant lentigines. Adopt healthy routines for the careful and protection of your skin contribute significantly to the prevention of these sun spots. Some tips key are:
- Use sunscreen daily: Include in your daily routine a high-quality sunscreen with sun protection factor sun protection (SPF) 50. This is the best measure to protect your skin from the harmful effects of the sun and prevent the skin cancer.
- Avoid hours of high radiation: Limit your sun exposure during the hours of greatest intensity, between 10 am and 4 pm, especially in months with high solar radiation.
- Use protective clothing and accessories: Wear wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses with UV protection, and long sleeves. bphysical attack against solar radiation.
- Consult your dermatologist: Visit your dermatologist regularly trusted to monitor the health of your skin to detect early significant changes in the spots and receive treatment.
Keep your skin well hydrated by rich diet in antioxidants, vitamins and minerals, as well as an adequate intake of water and healthy habitsBy avoiding tobacco, you contribute to welfare of your skin by preparing it and protecting its natural barrier.
Alarming signs
Although solar lentigo is usually benign, it can present malignant features in some cases. Therefore, it is essential to be attentive to any disturbance and consult your dermatologist if you observe any of the following abnormal features:
- Changes in the size and color, which may become irregular.
- Presence of fuzzy or asymmetrical edges.
- Changes in texture, such as the development of crusts or bleeding.
Furthermore, any skin lesion that presents these characteristics should be evaluated by a dermatologist, as it could indicate a serious skin problemEarly identification and diagnosis are crucial to avoid further complications.
In conclusion, the prevention To combat the appearance of solar lentigines and photoaging of the skin, protecting your skin from solar radiation is essential to reduce or prevent the formation of spots. At the García-Legaz Dermatological Institute, we understand the importance of a healthy skin tone. unified skin and we have specialists in clinical dermatology to help you maintain a healthy and radiant skin.
Literature
- Sánchez, GM Solar lentigo. DERMATOLOGICAL PATHOLOGY IN NON-CAUCASIAN PATIENTS, 51. https://www.sopeba.org
- Byrom, L., Barksdale, S., Weedon, D., & Muir, J. (2016). Unstable solar lentigo: a defined separate entity. Australasian Journal of Dermatology, 57(3), 229-234. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com
- Cardinali, G., Kovacs, D., & Picardo, M. (2012, December). Mechanisms underlying post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: lessons from solar lentigo. in Annales de Dermatologie et de Vénéréologie (Vol. 139, pp. S148-S152). Elsevier Masson. https://www.sciencedirect.com